HTML Introduction
HTML is the standard markup language. It looks like a skeleton for a website.
A simple HTML structure
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>Page title</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>My first heading</h1>
<p>My first paragraph</p>
</body>
</html>This is our code preview
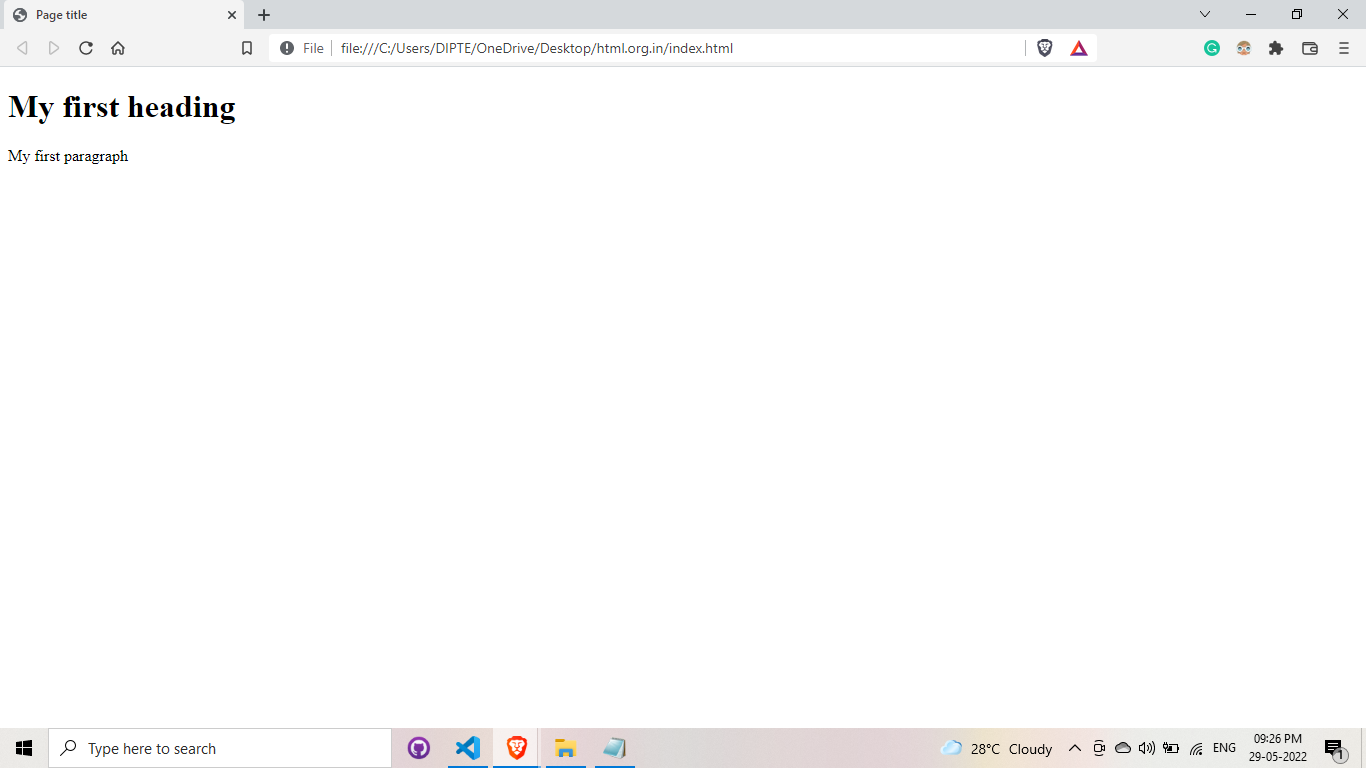
Let's talk about previous example
- <!DOCTYPE html> This is used to define that website is created with HTML5.
- <html> This is the root element.
- <head> This tag is used for add about website metadata and link stylesheet.
- <title> This tag is used to add website title.
- <body> We use this tag to add visible contents like images, paragraphs, hyperlinks, lists, tables, etc
- <h1> Element defines a large heading.
- <p> Element defines a paragraph.
Let's talk about How HTML Work & How we write.
HTML stands for hypertext markup language. When using HTML, we should keep in mind that every HTML element requires an opening & closing bracket. But there are some exceptions, such as [<br>, <hr>, <img>, <link>] etc. Tags like this are self-closing.
- This tag should be started with < this, then followed by your element argument, followed by> let's write it together "<html> " This is an opening tag. This tag should now be closed using the "/" symbol. What's the best way to do it? After the first bracket, we need to add "/" ,then followed by your element argument, followed by> let's write it together </html> This is the closing tag.
Let's discuss about the HTML history
- 1989 - Tim Berners-Lee invented www
- 1991 - Tim Berners-Lee invented HTML
- 1995 - HTML Working Group defined HTML 2.0
- 1997 - W3C Recommendation: HTML 3.2
- 1999 - W3C Recommendation: HTML 4.01
- 2000 - W3C Recommendation: XHTML 1.0
- 2008 - W3C HTML5 First Public Draft
- 2016 - W3C Candidate Recommendation: HTML 5.1